What is Java?
- Java is a general-purpose, object-oriented programming language.
- General Purpose means we can develop different types of applications using Java.
- In other words, Java is not domain-specific, so it can be used in various fields.
- Java language can be used for the following types of applications
- Desktop Applications
- Web Applications
- Enterprise Applications
- Mobile Applications
Editions of the Java Programming Language
- Java programming language has 3 different versions:
- JSE( Java Standard Edition)
- JSE is also known as core Java.
- JSE can be used to develop desktop applications.
- J2EE(Java Enterprise Edition)
- J2EE is also known as advanced Java.
- J2EE can be used to develop web applications.
- JME( Java Micro Edition)
- JME is also known as the Android edition.
- JME can be used for the development of an Android application.
Application Areas of Java
- Java can be used in the following fields.
- Desktop application development.
- Enterprise application development.
- Android application development.
- Automation tools.
- Big data technologies.
Features of Java
- Simple
- Java is a simple programming language because we can easily create and maintain Java syntax.
- It is possible to learn Java without knowing other programming languages.
- Platform independent
- Java is a platform-independent language; it means we can execute Java programs by using any OS platform.
- Portable
- Java is a portable programming language. It means we can switch the development environment from one operating system to another operating System
- In other words, we can develop Java applications by using various platforms.
- Object-oriented
- Java is an object-oriented programming language because we can represent everything in terms of objects.
- Multithreaded
- Java is a multi-threaded programming language, which means we can develop multi-threaded programs using Java. … Each of the threads can run in parallel.
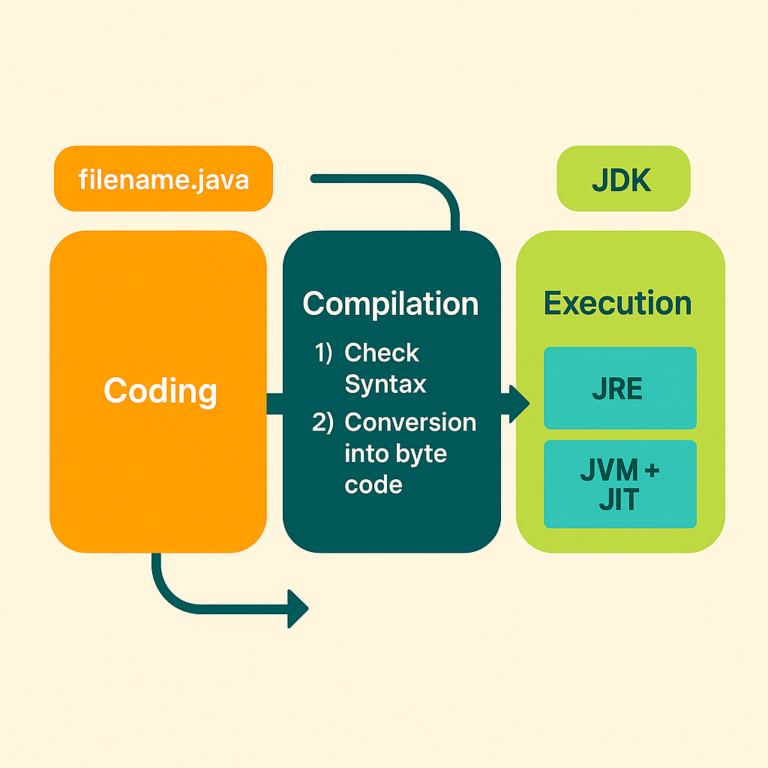
Development Process of Java Application
- Coding
- The process of writing Java statements inside the Java file is known as coding.
- The file that contains the source code is also known as the source file.
- Compilation
- After coding, we have to compile the .java file. The Java compiler is responsible for compilation.
- The Java compiler performs the following activities in order to complete the compilation process.
- Checks the syntax and rules of language.
- Converts Java statements into bytecode.
- After successful compilation, the compiler will generate a .class file.
- Execution
- JVM is responsible for the execution of the .class file.
- To complete the execution process, we have to install the JDK software.